Have you ever wondered what Frontend development is? The difference between Front-end and backend development? Read through as we break this down.
Front-end development is responsible for the interactive components, visual appeal, and simplicity of use that we all enjoy when browsing the web. Front-end developers are the creative minds who bring to life the user interface (UI) for websites and applications.
In simple terms, think of a website or app as a house. Back-end development establishes the foundation and plumbing, ensuring that everything runs properly. Front-end development, on the other hand, is similar to interior design and furnishing which determines the visual appeal, user experience (UX), and overall feel of the place.
At a point, developers have gotten lost in deciding which of these do they want to learn and be an expert in while some went ahead to be a Full-stack developer a combination of frontend and backend, some are proficient in Front-end development only while others choose backend. But what should influence your decision to be a frontend developer? We have highlighted everything you need to know about frontend. Starting from
- Fundamental Skills Needed to be a frontend developer
- Levels in Frontend Development
- How much do Frontend Developers earn? And
- How to get started as a frontend developer.
Core Skills for Front-End Developers:
Front-end development is based on several skills but the three essential languages are: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Mastering these core abilities is critical for creating appealing and functional user interfaces.
1. HTML – HTML, or HyperText Markup Language. HTML is the skeleton of a web page. It defines the structure and content of a webpage, using tags to specify headings, paragraphs, images, and more. Think of it as the blueprint that tells the browser where to place each element on the page. Somethings to note about HTML are
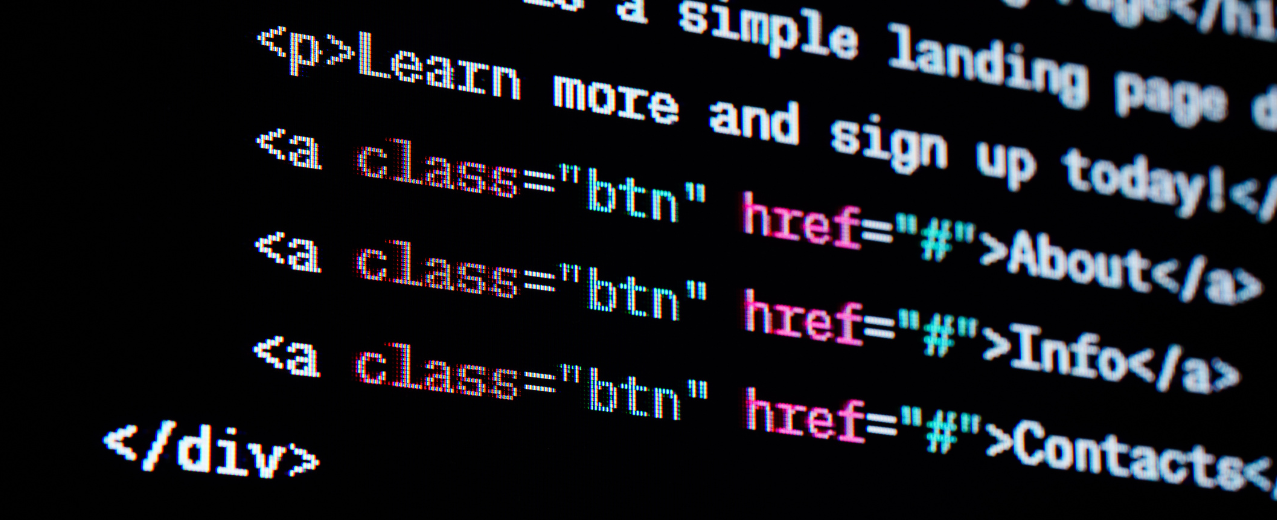
- Building Blocks: HTML uses tags, written in angle brackets (< >), to define different elements on a webpage. Common tags include <p> for paragraphs, <h1> for headings, <img> for images, and <a> for links. These tags tell the web browser how to interpret and display the content.
- Structure and Hierarchy: Tags can be nested within each other to create a hierarchy. For example, you might have a heading (<h1>) wrapped around a paragraph (<p>) to create a titled section. This nesting allows for organized and well-defined content.
- Attributes: Tags can have attributes like src for image location or href for link destination, providing extra information.
- Semantic Tags: Semantic tags like <h4> or <article> convey meaning beyond structure, improving readability and search engine understanding.
- Beyond Text: you can embed images, videos, audio, and even forms using specific tags to create a richer user experience.
This is just a bit of HTML’s capabilities! To truly master HTML and become a front-end developer, consider enrolling in a comprehensive front-end development course. These courses delve deeper into advanced concepts, explore real-world applications, and equip you with the skills to build professional-grade websites.
2. CSS – CSS or Cascading Style Sheets is the secret weapon of front-end developers, transforming plain HTML structures into visually stunning websites. It is used in changing text color, adding fancy fonts, or creating cool animations. CSS uses simple code to define styles. Some things to note about CSS include:
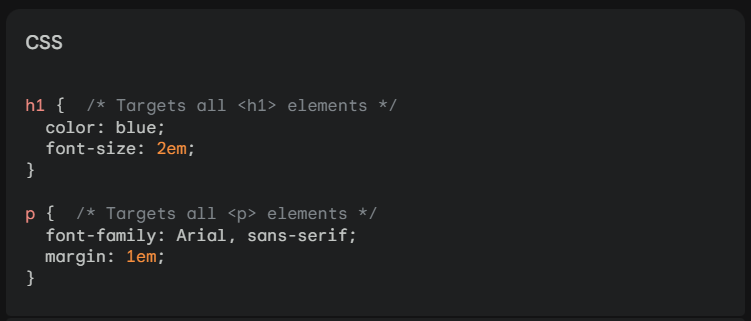
- Selector Specificity: Selectors choose which elements to style on a web page. More specific selectors (like .special-button) take priority over general selectors (like button) when applying styles.
- Responsive Magic: CSS lets you build responsive layouts that adapt to any screen size. Media queries allow you to define styles for different devices.
- Advanced Features: Animations, gradients, and pseudo-elements add a whole new level of creative control.
Mastering CSS empowers you to craft beautiful, user-friendly, and engaging web experiences. Want to make websites beautiful? start writing some CSS!
3. JavaScript (JS) – is the spark that ignites interactivity on web pages. It’s a dynamic programming language that allows you to add functionality beyond static HTML and styled CSS. Imagine click events, forms that respond to user input, or animations that come alive – that’s the power of JS. Here are somethings you can do with javascript: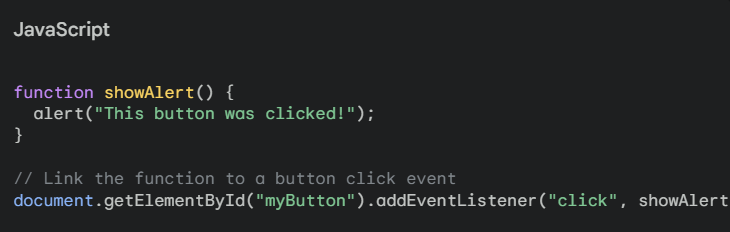
-
Adding Interactivity: With JS, you can create click events that trigger actions like displaying hidden content or redirecting to a new page.
-
Dynamic Content: JS can manipulate the content of a webpage, updating elements based on user interactions or external data.
-
Animations & Effects: Javascript can be used to add smooth animations and interactive elements to the webpage.
Levels in Front-end Development and How much they earn
Entry-Level Front-End Developer (Junior):
- Salary Range: ₦1,200,000 – ₦1,500,000 (Source: PayScale, Nigeria Salary Explorer)
- Skills: Strong foundation in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Basic understanding of frameworks and UI/UX principles.
-
Responsibilities: Assisting senior developers with coding tasks, building basic web page functionalities, and implementing pre-designed layouts.
Mid-Level Front-End Developer:
- Salary Range: ₦2,000,000 – ₦2,500,000 (Source: PayScale, Nigeria Salary Explorer)
- Skills: Proficient in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Experience with front-end frameworks like React or Angular. Strong understanding of UI/UX principles and responsive design.
-
Responsibilities: Independently building web pages and features, collaborating with designers and back-end developers, and ensuring website responsiveness across devices.
Senior Front-End Developer:
- Salary Range: ₦5,000,000 – ₦6,000,000 (Source: PayScale, Nigeria Salary Explorer)
- Skills: Expert-level proficiency in core languages and frameworks. Ability to lead and mentor junior developers, architect complex front-end solutions, and optimize website performance.
- Responsibilities: Leading front-end development projects, defining technical architecture, mentoring junior developers, and staying up-to-date with the latest front-end technologies.
These are general ranges, and salaries can vary depending on factors like location, company size, specific skill sets, and remote work opportunities (which can sometimes command higher salaries).
The journey in front-end development doesn’t stop here! As you gain experience and delve into specialized areas like front-end performance optimization or single-page applications, your earning potential can continue to climb. Keep learning, keep building, and watch your career in front-end development soar!
To learn the technologies of Front End Development mentioned in this roadmap of front end developers, you can check out WildFusion Digital Center Front End Online Course.








